Elderly Patients: Common Health Issues, Medication Risks, and Care Tips
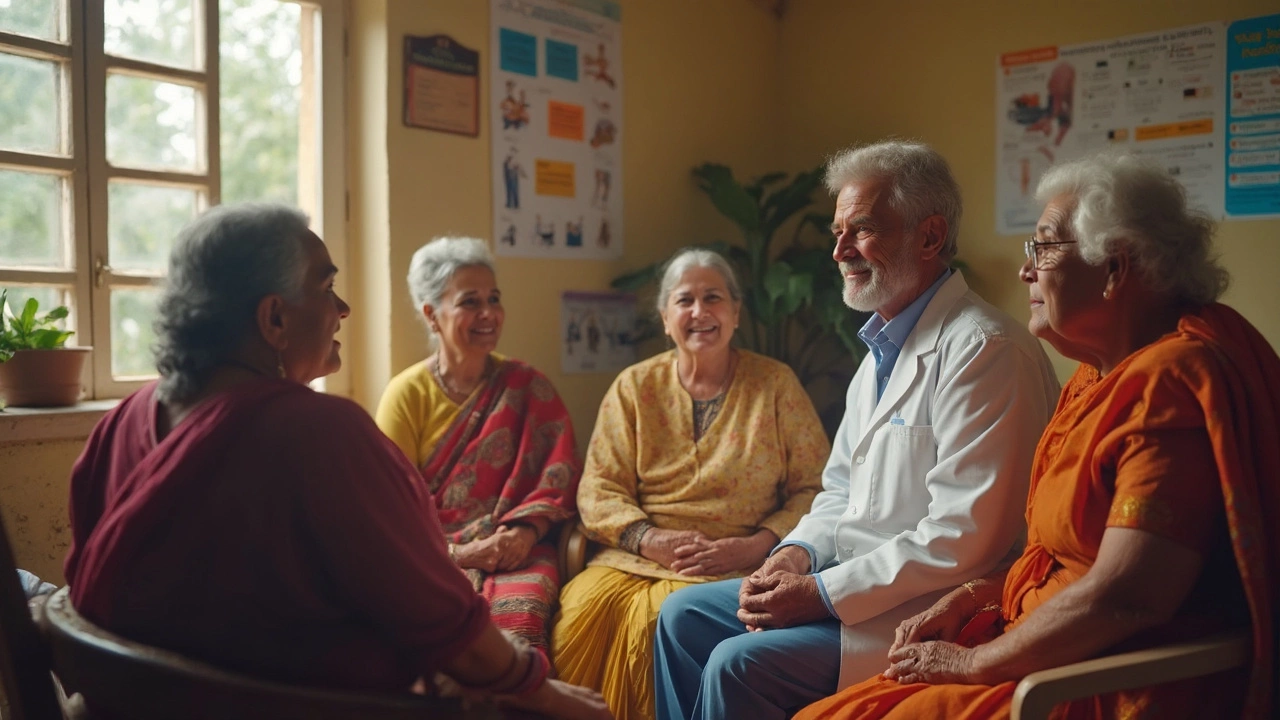
When we talk about elderly patients, older adults, typically aged 65 and above, who often manage multiple chronic conditions and complex medication regimens. Also known as senior patients, they face unique challenges in healthcare that younger adults rarely do. Their bodies process drugs differently, symptoms hide behind normal aging, and what looks like "just getting older" might be something serious.
Many chronic conditions in seniors, long-term illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, and dementia that require ongoing management overlap in elderly patients, making treatment tricky. A pill for high blood pressure might worsen kidney function. A supplement for sleep could spike anxiety. And because seniors often see multiple doctors, medications pile up—sometimes dangerously. This is why medication safety, the careful use, monitoring, and adjustment of drugs to avoid harm in older adults isn’t just important—it’s life-or-death. A simple mix of over-the-counter painkillers and blood thinners can lead to internal bleeding. A missed dose of insulin? That’s a hospital trip.
It’s not just about pills. geriatric care, specialized medical attention focused on the physical, mental, and social needs of older adults means looking at more than labs and scans. It’s asking: Can they get to the pharmacy? Do they remember to take their meds? Are they eating enough? Are they lonely? Depression in seniors often shows up as fatigue or confusion, not sadness. A fall isn’t just an accident—it’s a warning sign of muscle loss, poor balance, or even a heart rhythm issue. Many of the posts here dig into exactly these hidden problems: how diabetes acts differently in older bodies, why full blood tests catch things doctors miss, what herbs accidentally trigger anxiety in seniors, and how recovery from surgery takes longer—and needs more planning.
You won’t find fluffy advice here. Just real talk about what actually matters when you’re caring for someone older: spotting the signs early, avoiding dangerous drug combos, knowing when to push for more tests, and understanding that what works for a 40-year-old might hurt a 75-year-old. Whether you’re a family caregiver, a senior managing your own health, or a healthcare worker in India, the articles below give you the clear, practical details you need—no jargon, no fluff, just what works.
What Age Is Too Old for Knee Replacement Surgery?
Wondering at what age doctors stop doing knee surgery? This article breaks down common myths about age limits, dives into what really matters for knee replacement eligibility, and looks at how older adults can recover well. You'll find real numbers, doctor advice, and tips to help you or a loved one make the best choice. No technical jargon—just the facts and some first-hand insight. Perfect if you want honest, clear answers without the runaround.